Is Acidity A Physical Property
Essential Ideas
Physical and Chemical Properties
OpenStaxCollege
[latexpage]
Learning Objectives
By the finish of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify backdrop of and changes in affair as physical or chemical
- Identify properties of matter as all-encompassing or intensive
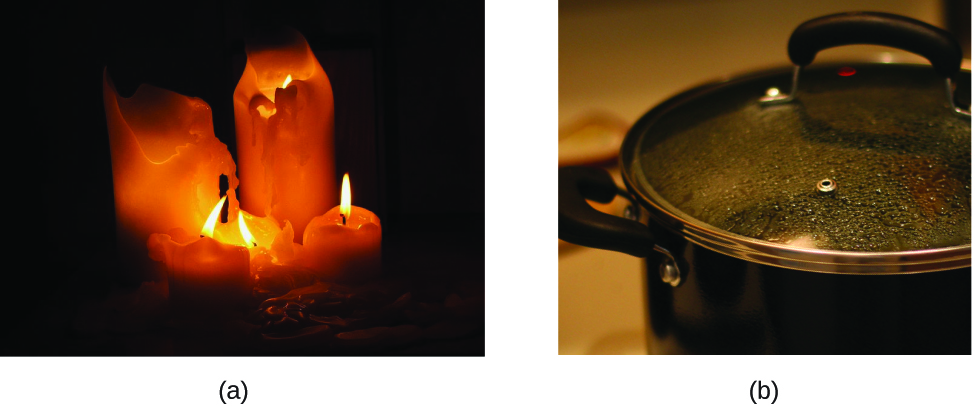
The characteristics that enable us to distinguish one substance from another are chosen properties. A concrete belongings is a characteristic of thing that is non associated with a alter in its chemic composition. Familiar examples of physical properties include density, color, hardness, melting and boiling points, and electrical conductivity. We can observe some physical backdrop, such as density and color, without changing the physical land of the matter observed. Other physical properties, such as the melting temperature of iron or the freezing temperature of water, tin can only be observed as matter undergoes a physical modify. A physical change is a change in the land or properties of thing without whatsoever accompanying change in its chemical limerick (the identities of the substances independent in the thing). We detect a physical change when wax melts, when sugar dissolves in coffee, and when steam condenses into liquid h2o ([link]). Other examples of physical changes include magnetizing and demagnetizing metals (equally is done with common antitheft security tags) and grinding solids into powders (which can sometimes yield noticeable changes in color). In each of these examples, there is a change in the physical state, course, or properties of the substance, but no change in its chemic limerick.
(a) Wax undergoes a concrete alter when solid wax is heated and forms liquid wax. (b) Steam condensing within a cooking pot is a concrete change, as water vapor is changed into liquid water. (credit a: modification of work by "95jb14"/Wikimedia Eatables; credit b: modification of work by "mjneuby"/Flickr)

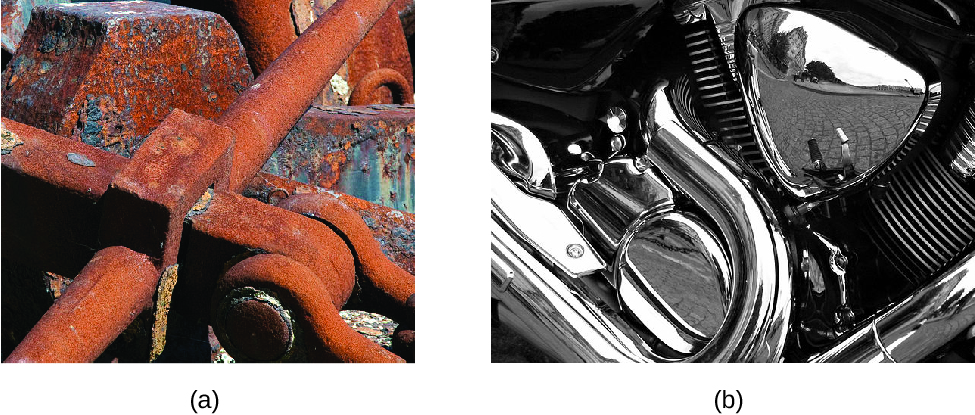
The alter of ane blazon of affair into another blazon (or the inability to alter) is a chemical property. Examples of chemical properties include flammability, toxicity, acidity, reactivity (many types), and rut of combustion. Iron, for example, combines with oxygen in the presence of water to form rust; chromium does not oxidize ([link]). Nitroglycerin is very dangerous because it explodes easily; neon poses about no hazard because information technology is very unreactive.
(a) One of the chemical properties of iron is that it rusts; (b) ane of the chemical properties of chromium is that information technology does not. (credit a: modification of work past Tony Hisgett; credit b: modification of work by "Atoma"/Wikimedia Eatables)

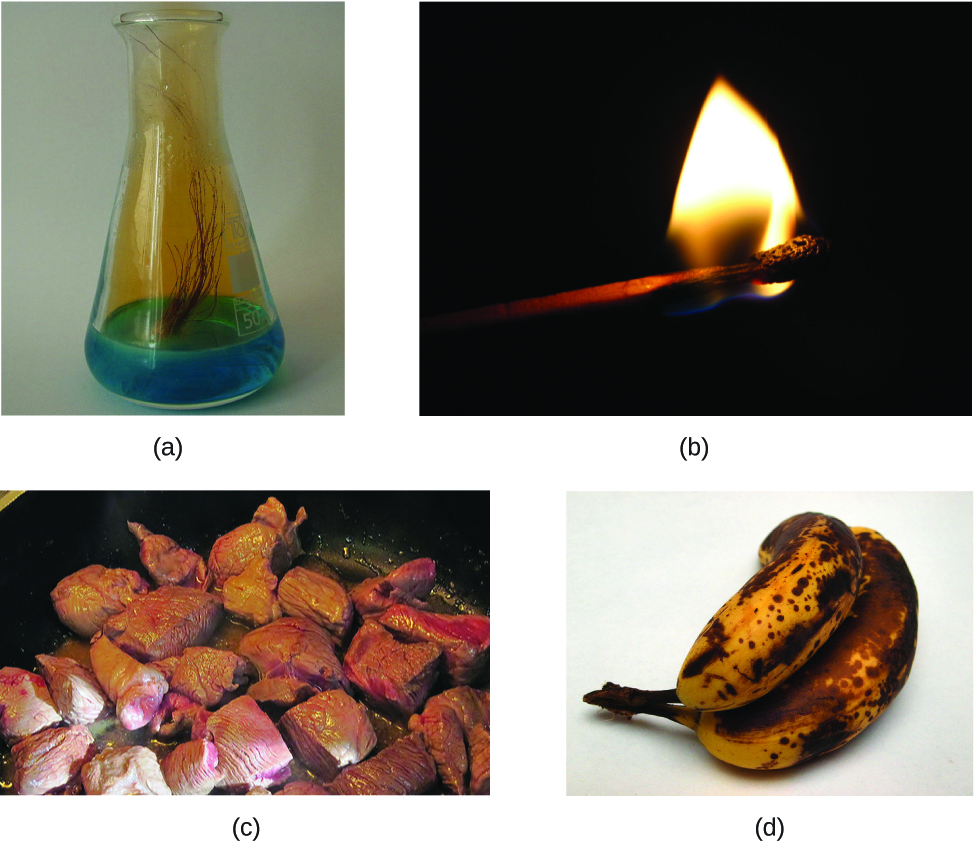
To identify a chemical property, nosotros await for a chemical change. A chemic change always produces one or more types of matter that differ from the matter present before the change. The formation of rust is a chemic change because rust is a different kind of matter than the iron, oxygen, and water nowadays before the rust formed. The explosion of nitroglycerin is a chemical change considering the gases produced are very different kinds of affair from the original substance. Other examples of chemical changes include reactions that are performed in a lab (such as copper reacting with nitric acid), all forms of combustion (called-for), and food beingness cooked, digested, or rotting ([link]).
(a) Copper and nitric acid undergo a chemical modify to form copper nitrate and dark-brown, gaseous nitrogen dioxide. (b) During the combustion of a match, cellulose in the match and oxygen from the air undergo a chemical change to form carbon dioxide and water vapor. (c) Cooking red meat causes a number of chemical changes, including the oxidation of iron in myoglobin that results in the familiar cerise-to-brownish colour change. (d) A assistant turning brown is a chemical alter as new, darker (and less tasty) substances form. (credit b: modification of piece of work past Jeff Turner; credit c: modification of work by Gloria Cabada-Leman; credit d: modification of work past Roberto Verzo)

Backdrop of thing fall into 1 of two categories. If the property depends on the amount of affair present, it is an extensive belongings. The mass and volume of a substance are examples of extensive properties; for instance, a gallon of milk has a larger mass and book than a cup of milk. The value of an all-encompassing belongings is direct proportional to the amount of matter in question. If the property of a sample of thing does not depend on the amount of matter present, information technology is an intensive property. Temperature is an example of an intensive belongings. If the gallon and cup of milk are each at 20 °C (room temperature), when they are combined, the temperature remains at twenty °C. Every bit another example, consider the distinct merely related backdrop of heat and temperature. A drop of hot cooking oil spattered on your arm causes brief, pocket-sized discomfort, whereas a pot of hot oil yields severe burns. Both the drop and the pot of oil are at the same temperature (an intensive property), but the pot clearly contains much more heat (extensive property).
Take chances Diamond
Yous may have seen the symbol shown in [link] on containers of chemicals in a laboratory or workplace. Sometimes called a "fire diamond" or "hazard diamond," this chemic hazard diamond provides valuable information that briefly summarizes the various dangers of which to be enlightened when working with a particular substance.
The National Fire Protection Agency (NFPA) take a chance diamond summarizes the major hazards of a chemical substance.
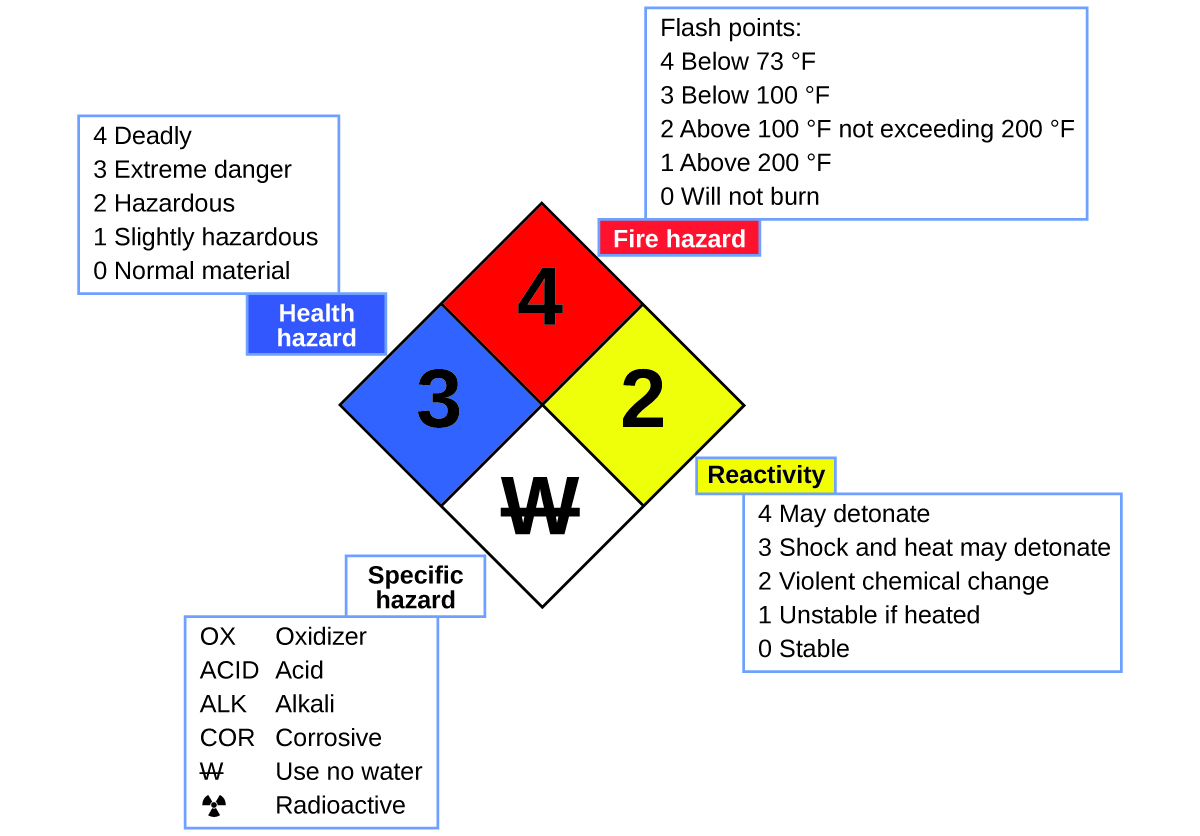
The National Burn Protection Bureau (NFPA) 704 Risk Identification Organisation was developed by NFPA to provide rubber information virtually sure substances. The system details flammability, reactivity, wellness, and other hazards. Within the overall diamond symbol, the pinnacle (scarlet) diamond specifies the level of burn down take a chance (temperature range for flash signal). The blueish (left) diamond indicates the level of health hazard. The yellow (right) diamond describes reactivity hazards, such equally how readily the substance will undergo detonation or a tearing chemical alter. The white (lesser) diamond points out special hazards, such as if information technology is an oxidizer (which allows the substance to fire in the absence of air/oxygen), undergoes an unusual or dangerous reaction with h2o, is corrosive, acidic, alkaline metal, a biological risk, radioactive, and so on. Each hazard is rated on a scale from 0 to 4, with 0 being no take chances and iv being extremely hazardous.
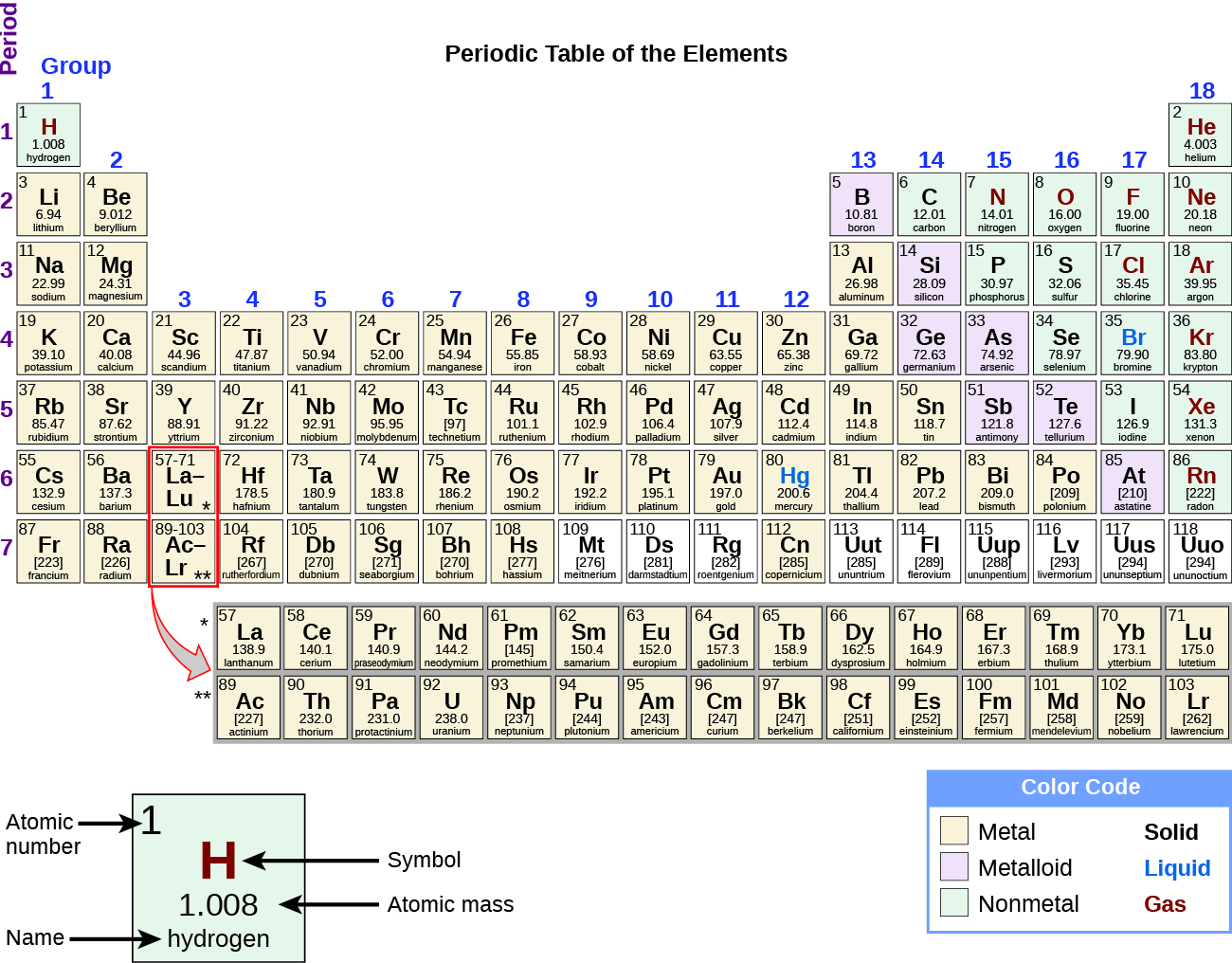
While many elements differ dramatically in their chemic and physical properties, some elements have similar backdrop. We tin can identify sets of elements that exhibit mutual behaviors. For example, many elements conduct oestrus and electricity well, whereas others are poor conductors. These properties can be used to sort the elements into three classes: metals (elements that conduct well), nonmetals (elements that conduct poorly), and metalloids (elements that take backdrop of both metals and nonmetals).
The periodic table is a table of elements that places elements with similar properties close together ([link]). You will acquire more almost the periodic table as you continue your report of chemistry.
The periodic table shows how elements may be grouped according to certain similar properties. Notation the background color denotes whether an chemical element is a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal, whereas the chemical element symbol color indicates whether it is a solid, liquid, or gas.
Key Concepts and Summary
All substances have distinct physical and chemical properties, and may undergo physical or chemical changes. Physical properties, such equally hardness and boiling betoken, and physical changes, such as melting or freezing, do non involve a change in the composition of matter. Chemical properties, such flammability and acidity, and chemical changes, such equally rusting, involve production of matter that differs from that present beforehand.
Measurable properties fall into one of 2 categories. Extensive properties depend on the amount of thing present, for instance, the mass of gold. Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter nowadays, for example, the density of gold. Heat is an instance of an extensive holding, and temperature is an example of an intensive belongings.
Chemical science End of Affiliate Exercises
Classify the half dozen underlined properties in the post-obit paragraph as chemic or physical:
Fluorine is a stake yellow gas that reacts with most substances. The complimentary element melts at −220 °C and boils at −188 °C. Finely divided metals fire in fluorine with a vivid flame. Nineteen grams of fluorine will react with 1.0 gram of hydrogen.
Allocate each of the post-obit changes equally physical or chemical:
(a) condensation of steam
(b) burning of gasoline
(c) souring of milk
(d) dissolving of sugar in water
(eastward) melting of gold
(a) physical; (b) chemical; (c) chemical; (d) physical; (e) physical
Classify each of the following changes as physical or chemic:
(a) coal burning
(b) water ice melting
(c) mixing chocolate syrup with milk
(d) explosion of a firecracker
(due east) magnetizing of a screwdriver
The volume of a sample of oxygen gas changed from 10 mL to xi mL as the temperature inverse. Is this a chemical or physical change?
physical
A two.0-liter volume of hydrogen gas combined with 1.0 liter of oxygen gas to produce two.0 liters of h2o vapor. Does oxygen undergo a chemical or physical modify?
Explain the difference between extensive properties and intensive properties.
The value of an extensive belongings depends upon the amount of thing being considered, whereas the value of an intensive property is the same regardless of the amount of affair being considered.
Identify the following properties as either extensive or intensive.
(a) volume
(b) temperature
(c) humidity
(d) oestrus
(e) boiling point
The density (d) of a substance is an intensive property that is defined as the ratio of its mass (thou) to its volume (5).
\(\text{density}=\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\frac{\text{mass}}{\text{book}}\phantom{\rule{2em}{0ex}}\text{d}=\phantom{\dominion{0.2em}{0ex}}\frac{\text{chiliad}}{\text{V}}\)
Because that mass and volume are both all-encompassing properties, explain why their ratio, density, is intensive.
Beingness extensive properties, both mass and volume are straight proportional to the amount of substance under study. Dividing i extensive holding by another will in consequence "cancel" this dependence on corporeality, yielding a ratio that is contained of amount (an intensive property).
Glossary
- chemical modify
- alter producing a different kind of matter from the original kind of thing
- chemical property
- behavior that is related to the change of one kind of thing into another kind of matter
- extensive property
- property of a substance that depends on the amount of the substance
- intensive property
- property of a substance that is contained of the amount of the substance
- physical change
- change in the country or properties of matter that does not involve a modify in its chemical composition
- physical property
- feature of affair that is non associated with whatsoever change in its chemic composition
Is Acidity A Physical Property,
Source: https://pressbooks-dev.oer.hawaii.edu/chemistry/chapter/physical-and-chemical-properties/
Posted by: baltzcoonly63.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is Acidity A Physical Property"
Post a Comment